Assalamualaikum,
Business Level Strategy
- Refers to strategies that firms use to
build competitive advantage.
- Focus on improving competitive position of a company's product or services within the specific industry or market segment that the company services.
Micheal Porter presented 2 generic business level strategies:
- Cost leadership
- Differentiation
- Focus strategy
Cost Leadership Strategy
- It refers to the organization ability to produce a product or service at a cost below what competitors can achieve.
- Companies which utilize Cost Leadership Strategy would concentrate on providing a basic and standardized product or services that can be produced at a relative low cost and made available to a broad target market.
- Successful implementation requires a consistent focus on driving cost relatively lower to competitors' cost.
Example of Company:
- MyDin
- McDonald
- Dell
- Air Asia
Differentiation Strategy
- Consists of creating differences in the firm's products or services by offering something that is perceived industry wide as unique and valued by customers.
- Firms that use this strategy would emphasize brand image, unique styling, technology, features, a dealer network, customer service or innovative design.
- This strategy is based on assumption that customers are willing to pay a higher price for a product or service that is distinct or perceived to be unique from that of its rivals.
- Differentiation strategy create customer loyalty to a firm's products because customer perceived this products to be unique and as a result, are willing to pay more.
- Firms that use this strategy should constantly upgrade the differentiated features that customers value without significant cost increase.
Example of Company:
- Rolex
- FedEx
- Apple
- Sony
- Harley Davidson
- Louis Vuitton
Focus Strategy
- Based on the firm competing on a narrow scope within an industry where the firm selects a segment or group and tailors its strategy to serve them.
- The success of a focus strategy rest's on the firm's ability to identify segments that are not properly served or to find market segment that have unique needs or that are so specialized that broad-based competitors select not to serve them.
- Firms that follows focus strategy earn high profitability by meeting the needs of a particular buyer group, having the ability to attract a growing number of a new customers, and continuing to attract repeat customers.
Example of Company:
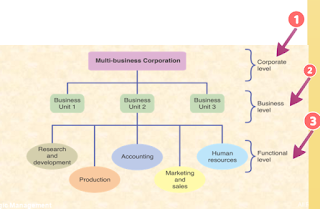
Functional Level Strategies
- Actions taken at the functional or operation level and the must be in line or contribute towards the overall strategy of corporation.
- The functional strategies address problems commonly face by lower-level managers and handle activities considered relevant to achieve the business level and corporate level strategies.
- The functional level of organization is the level operating division and department.
- The Value Chain Analysis (VCA) is a systematic approach to examine the development of competitive advantage.
The Value Chain
- The value chain activities can be classified into two main categories, primary activities and support activities.